Process Management in Linux – Monitoring & Controlling Processes
🔹 Introduction
Process Management in Linux: Every program running on a Linux system is a process. Some processes run in the foreground, while others operate in the background to manage critical system functions. Properly monitoring and controlling these processes ensures that your system runs smoothly and efficiently.
💡 Why Process Management is Important?
- Helps identify performance bottlenecks
- Allows prioritization of important tasks
- Prevents system crashes due to high resource usage
- Enables better troubleshooting of system issues
This guide will teach you how to:
✅ Monitor running processes using ps, top, and htop
✅ Control processes with kill, nice, renice, and nohup
✅ Manage background and foreground tasks
✅ Optimize CPU and memory usage
1️⃣ Understanding Linux Processes
🔹 What is a Process?
A process is simply an instance of a running program. Each process in Linux is assigned a Process ID (PID) and has an associated user, priority level, and resource consumption.
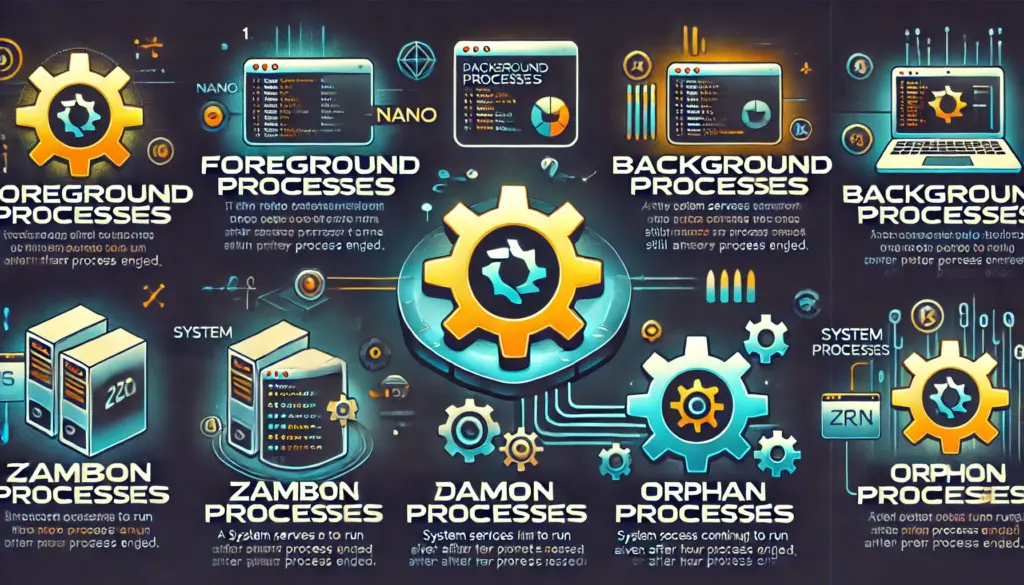
🔹 Types of Linux Processes
🔹 Foreground Processes: Require user interaction (e.g., text editors like nano or vim).
🔹 Background Processes: Run in the background without direct user interaction (e.g., web servers, cron jobs).
🔹 Daemon Processes: Special background processes that start during system boot (e.g., sshd, crond).
🔹 Zombie Processes: Completed but still listed in the process table.
🔹 Orphan Processes: The parent process is terminated, but the child continues running.
2️⃣ How to Monitor Running Processes in Linux
🔹 Viewing a List of Running Processes (ps Command)
The ps command is used to display information about running processes.
📌 Basic usage:
ps aux📌 Understanding the output:
| Column | Meaning |
|---|---|
USER | User who owns the process |
PID | Process ID |
%CPU | CPU usage of the process |
%MEM | Memory usage of the process |
COMMAND | Command that started the process |
🔹 Real-Time Process Monitoring (top Command)
The top command provides an interactive, real-time view of running processes, updating live.
📌 Run the command:
top📌 Key actions in top:
- Press
qto quit - Press
k, enter PID to kill a process - Press
Mto sort by memory usage
🔹 Advanced Process Monitoring with htop
htop is an interactive alternative to top with color-coded output and easier process management.
📌 Install htop
sudo apt install htop # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo yum install htop # CentOS/RHEL
htop📌 Features of htop:
✔️ Scrollable list of processes
✔️ Kill processes with function keys
✔️ Display CPU & memory usage per process
3️⃣ Managing Processes in Linux
🔹 How to Kill a Process (kill, pkill, killall)
Sometimes, a process consumes too many resources or becomes unresponsive. You can terminate it using these commands:
🔹 Kill a process by PID:
kill <PID>🔹 Kill a process by name:
pkill process_name🔹 Force kill a process:
kill -9 <PID>🔹 Kill all instances of a process:
killall process_name🔹 Adjusting Process Priority (nice and renice)
Processes have a priority level that determines how much CPU time they get.
📌 Check a process’s priority:
ps -o pid,ppid,ni,cmd -p <PID>📌 Run a process with lower priority:
nice -n 10 command📌 Change priority of a running process:
renice -n 5 -p <PID>4️⃣ Running Processes in Background & Foreground
🔹 Run a Command in the Background (&)
sleep 60 &🔹 Bring a Background Process to Foreground (fg)
fg %1🔹 Keep a Process Running After Logout (nohup)
nohup command &📌 This prevents the process from stopping when you log out.
5️⃣ Troubleshooting High CPU & Memory Usage
🔹 Find High CPU Usage Processes
ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%cpu | head🔹 Find High Memory Usage Processes
ps -eo pid,ppid,cmd,%mem,%cpu --sort=-%mem | head🔹 Check System Load Average
uptime📝 Summary
🔹 Process monitoring: ps, top, htop
🔹 Process control: kill, pkill, killall, nice, renice
🔹 Background & foreground processes: bg, fg, nohup
🔹 Troubleshooting: Identify high CPU/memory processes
💬 Have questions? Drop them in the comments below!
📌 Call to Action:
🔗 Want more Linux guides? Subscribe to TechNops.com for daily updates! 🚀